Table of contents
No headings in the article.
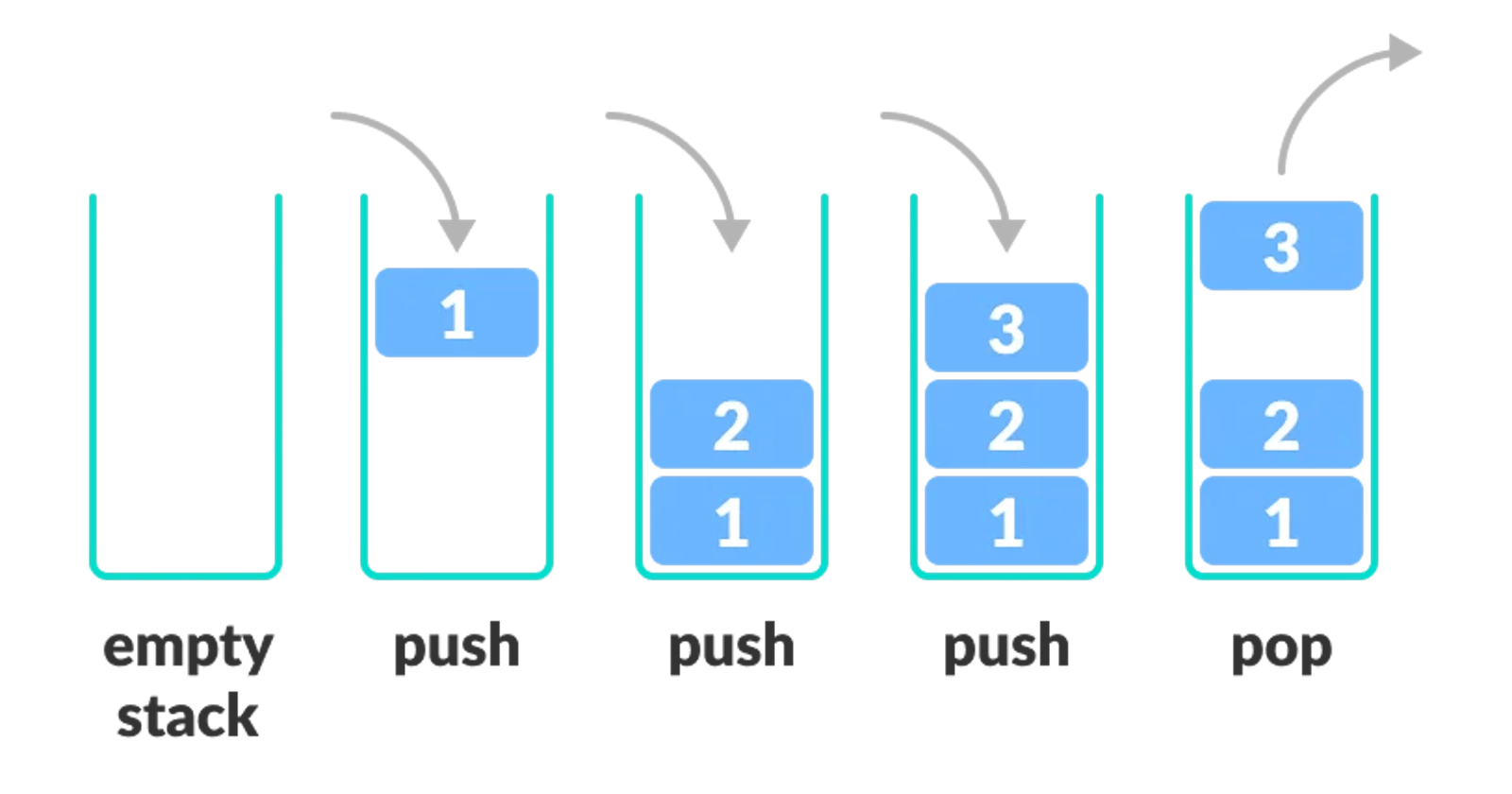
Imagine you have a stack of plates in front of you. You can only add or remove plates from the top of the stack. A stack in computer science is similar! It's a way of organizing data where you can only add or remove items from the top.
🍽️ How does a stack work?
Let's say you have a stack of 3 plates. You start by adding a plate to the top, then another plate, and finally a third plate. When you want to remove a plate, you always take the one from the top.
🔢 Basic Operations on a Stack:
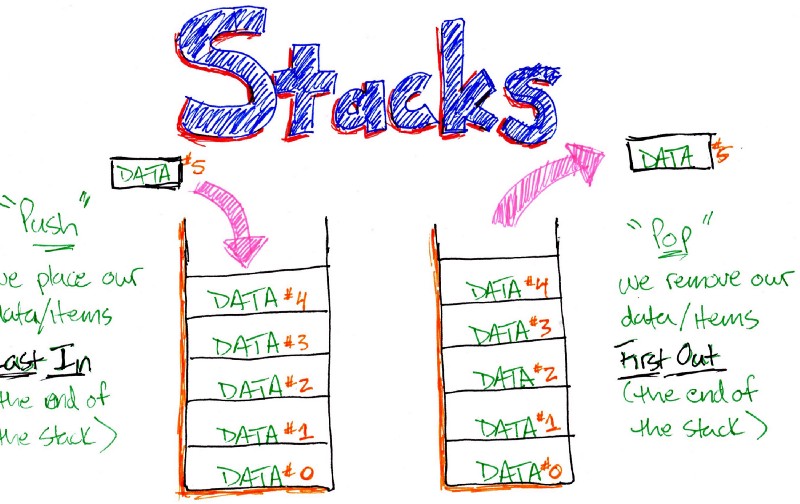
1️⃣ Push: Adding an item to the stack. You put a new plate on top of the stack.
2️⃣ Pop: Removing an item from the stack. You take the top plate off the stack.
3️⃣ Top: Checking what item is on the top of the stack without removing it.
4️⃣ isEmpty: Checking if the stack is empty (has no plates) or not.
5️⃣ Size: Counting how many plates are in the stack.
🧩 Real-Life Examples:
Stacks are everywhere! Think of a pile of books, where you can only add or remove a book from the top. Or think of a stack of pancakes, where you can only eat the top one. Stacks are also used in many computer programs and algorithms!
🤖 Implementation of a Stack:
There are different ways to implement a stack. One way is to use an array, like stacking plates on a table. You can also use a linked list, where each item in the stack points to the item below it.
Here's an example of implementing a stack using an array in the C++ programming language:
// Create a Stack class
class Stack {
int top;
public:
int a[MAX]; // Maximum size of the Stack
Stack() { top = -1; }
bool push(int x);
int pop();
int peek();
bool isEmpty();
};
// Implement the basic stack operations (push, pop, peek, isEmpty)
// Create a stack object and perform operations on it
Stack s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
cout << s.pop() << " popped from stack\n";
cout << "Top element is: " << s.peek() << endl;
cout << "Elements present in stack: ";
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
cout << s.peek() << " ";
s.pop();
}
🎯 Advantages and Disadvantages:
Using an array to implement a stack is easy and saves memory, but it has a fixed size. Using a linked list allows the stack to grow or shrink dynamically, but it requires more memory for storing pointers.
📚 Applications of Stacks:
Stacks have many applications in computer science:
📝 Infix to Postfix or Prefix conversion: Converting mathematical expressions into a different form. 🔄 Undo and Redo: Used in text editors or software to undo or redo actions. ⏪ Back and Forward buttons in web browsers: Stacks keep track of visited pages. 🧠 Function calls: Stacks help manage the order of function calls in computer programs. 🧱 Memory management: Stacks are used to allocate and deallocate memory in computer systems. 🎮 Game algorithms: Stacks are used in games like chess or checkers to make decisions and explore different paths. 🏗️ And many more!
That's it! Now you know what a stack is, how it works, and where it's used. So, next time you see a